Alliaria petiolata
By Victoria Wallace, Alyssa Siegel-Miles, and Klaudia Sowizral, UConn Extension
Identifying Features
- OVERVIEW: A vigorous, multi-stemmed biennial (two years to mature and set seed). Laboratory studies have found that garlic mustard releases chemicals that can inhibit the growth of neighboring plant species. A single plant can populate or repopulate an entire site.
- LEAVES: First year, basal rosette foliage is rounded with toothed margins. Up to 4 in. in diameter. The main leaf veins arise from a single point. Foliage has an odor of garlic when crushed. Basal rosettes remain green through fall and winter. Second year leaves on flower stalks are triangular, smaller, and alternately arranged.
- FLOWERS: Four-petaled white flowers appear in May to June on a stem above the foliage. Flower stalks emerge from the basal rosette in early spring of the second year and the plant dies after setting seed. Flower stalks can grow to a height of up to 3 ft., however, flowers can also appear on much shorter stems. Garlic mustard is commonly the only tall, broad-leafed, four-petaled white woodland plant blooming in early spring. Flowers are either self-pollinated or cross-pollinated by insects.
- SEED/FRUIT: The seed pods (siliques) are long, narrow, four-sided and contain rows of small, black, oblong seeds.
- ROOTS: White tap root has an S-shaped curve at the top.
- REPRODUCTION: Reproduces by seed only. An average, single plant produces between 600-7,500 seeds. Soil disturbance aids in seed germination and establishment; populations are greater in disturbed sites.




Habitat
Garlic mustard can thrive in a variety of climates and grows in full sun to full shade. It can survive in relatively dry to wet soil. The plant grows most aggressively in woodland areas with moist soil. It shoots up in early spring, posing a particular threat to spring ephemeral wildflowers.
Control
MECHANICAL:
Can be easily hand-pulled during the growing season. Scout for and pull garlic mustard in locations with few plants to control new invasions. Once flowers are evident, place removed plant material in bags and dispose of in garbage. Plants can also be repeatedly cut at the ground level prior to seed formation (before May). Reduction of an extensive seedbank will require at least 5-10 years of consistent effort and sites should be monitored in following years. Research from Cornell University asserts that mechanical control of garlic mustard-infested are-as is counterproductive, causing soil disturbance that encourages more growth of garlic mustard, while established garlic mustard populations decline with time on their own.
CHEMICAL:
Follow label instructions for all applications. For large populations, a foliar application of a non-selective herbicide (e.g., glyphosate), may be recommended. Applications made during the early spring (March-April), when garlic mustard is one of the few plants actively growing, are less likely to injure native plant material (be alert for emerging native plant growth).
DIRECTED BURNING:
Prescribed fires have been considered as a means of control; however, effectiveness has been found to vary. Burning is most effective in fire-dependent plant communities, where native plants are able to germinate and re-establish after a fire. A single directed burning will not by itself eliminate an established garlic mustard population. However, repeated fires to suppress garlic mustard may be detrimental to existing or emerging native plants. Flame weeding may be considered as a first step in a control strategy, followed by hand-pulling in subsequent years.
BIOLOGICAL CONTROL:
In Europe, populations of garlic mustard are managed by many native biological enemies. To date, in the United States, viable biological control options are still being evaluated.
Refer to CIPWG’s Invasive Plant Management Calendar for more information (cipwg.uconn.edu).
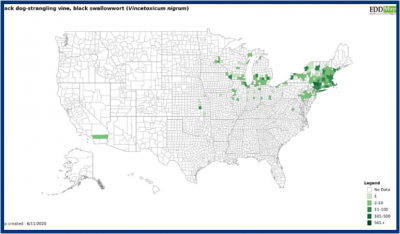
Distribution
Garlic mustard is commonly found in the Northeastern U.S., south to Georgia, and scattered throughout the Midwest and regions in the Pacific northwest.
Background
Garlic mustard is native to Europe and parts of Asia. Originally introduced from Europe as a source of food, the plant was first recorded in North America in Long Island, New York in 1868. Garlic mustard is edible for humans but eaten by few native insect or animal species. Lack of predation has contributed to its ability to take over many woodland areas in the northeast.
SOURCES:
- Connecticut Invasive Plants Council. (2018, October). Connecticut Invasive Plant List. https://cipwg.uconn.edu/
- Cavara & Grande (n.d.). Garlic mustard: Alliaria petiolata (Bieb.) Invasive.org. Retrieved April 2021 from https://www.invasive.org/browse/subinfo.cfm?sub=3005
- Munger, G. T. (2001). Alliaria petiolata. Fire Effects Information System, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station, Fire Sciences Laboratory. https://www.fs.usda.gov/database/feis/plants/forb/allpet/all.html
- New York Invasive Species (IS) Information. (2019, July 2). Garlic Mustard. Cornell Cooperative Extension & SeaGrant New York. https://nyis.info/species/garlic-mustard/#:~:text=Garlic%20mustard%20is%20a%20non,1868%20on%20Long%20Island%2C%20NY
- NY Invasives. (2021, February 26). When Doing Nothing is the Best Invasive Plant Management Tool [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vRQal0Hq5nM
- Sabin, I. O. & Polanin, N. (2013, September). Identification, Control, and Impact of Garlic Mustard, Alliaria petiolata. Rutgers Cooperative Extension Fact Sheet FS1212. New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station. https://njaes.rutgers.edu/fs1212/
Questions? Contact:
Vickie Wallace
UConn Extension
Extension Educator
Sustainable Turf and Landscape
Phone: (860) 885-2826
Email: victoria.wallace@uconn.edu
Web: ipm.uconn.edu/school
UConn Extension is committed to providing equal access and full participation for individuals with disabilities within all our programs and activities. Visit s.uconn.edu/accessibility for more resources. UConn is an equal opportunity program provider and employer.
Funds to support the creation of this document were provided by the Crop Protection and Pest Management Extension Implementation Program [grant no. 2017-70006-27201/project accession no. 1013777] from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
©UConn Extension. All rights reserved.
Updated April 2021
  |